
|
All three texts reveal currents of feeling and thought that are distrustful
of language. Pessoa poses his point, in his broad appeal to the reader—"all
of us," that is—as a general human condition. He suspects that in all of
us thoughts run like a parallel stream beside a "life that is lived." Language
has its own independent logic. We tell stories about ourselves, define
experiences, judge events, and give voice to our feelings. Yet what we
tell ourselves follows on the structure of language as given to us. The
murky liquid dynamism of life is poured into the ready mold of language
without convincing us that something is not left out in the shape assumed.
The events of our life take on the form of known narrative structures.
We imagine in the events of our lives the shadow of a bildungsroman,
a cinematic melodrama or life as advertised. Ready words name our sentiments
and we love, miss, and grow angry—whatever—according to the elaborate histories
connected to the words that name these sentiments. Meaning—even that conveyed by a rudimentary individual word—is divided
up in certain arbitrary ways, as a simple attempt at translation from one
language to another readily demonstrates. Although inevitably and endlessly
falling prey to the preformed patterns of thought, intimations of another
life shimmer out of thought's reach on the horizon of consciousness. (Pessoa's
trickiness lies in not calling that sense of the incommensurate the glimmerings
of a truer life, but pointedly supposes that no such judgment is possible:
"But which is true / And which is false / Nobody can explain").
Meaning—even that conveyed by a rudimentary individual word—is divided
up in certain arbitrary ways, as a simple attempt at translation from one
language to another readily demonstrates. Although inevitably and endlessly
falling prey to the preformed patterns of thought, intimations of another
life shimmer out of thought's reach on the horizon of consciousness. (Pessoa's
trickiness lies in not calling that sense of the incommensurate the glimmerings
of a truer life, but pointedly supposes that no such judgment is possible:
"But which is true / And which is false / Nobody can explain").
Alvaro Siza's and Fernando Tavora's statements suggest that something
analogous has occurred in architecture. Tavora rejects what he calls "style,"
which is really expression that no longer seems properly linked to its
content—expression that seems superfluous to meaning, mere flourishes.
He instead favors something that will grow out of the relationship between
"work and life." Siza, a student of Fernando Tavora and a lifelong friend,
echoes the older architect's sentiment: he rejects "pre-established language"
and seeks to respond to a "concrete problem, a situation in transformation
in which I participate." In architecture they aim for that utopia where
form would be neither an arbitrary inheritance nor an arbitrary system
of forms, but would grow directly out of our needs, and those needs' interaction
with our environments, and most generally (if also most vaguely) out of
who we are. |
|
Yet what does all that mean? It reminds me of an analogous ambition
ascribed to the "American action painting" of Pollack, Kline, de Kooning,
etc., by their champion and critic, Harold Rosenberg. He said that this
painting "at its inception was a method of creation—not a style or look
that pictures strove to achieve." 4
The paintings were records of human gesture unmediated by the treacherous
pressure of thought and preconceived images. These paintings, like the
track left behind a figure skater, recorded life itself unfolding. |

 1.
Bairro do Alvito (plan and photo)
1.
Bairro do Alvito (plan and photo)
 2.
Praca do Imperio e Exposicao do Mundo Portugues (photo)
2.
Praca do Imperio e Exposicao do Mundo Portugues (photo)
|
But what could this mean in relationship to architecture,
an art that is by its very definition premeditated? First we draw, then
someone following what amounts to instructions must build. Architecture
is neither a very spontaneous process nor is it very receptive to those
patent contrivances that try to transpose "automatic" drawings to the built
realm. To understand how these statements, or theoretical ambitions, relate
to architecture, and to understand what consequences they finally had on
Alvaro Siza's work, we will have to trace two parallel histories. The first
relates to the understanding developed by the previous generation of Portuguese
architects—among whom Tavora played a significant role—of Portuguese vernacular
architecture,  and of the impact it had on their thinking. The other historical thread
that needs pursuing relates to the development of the architectural promenade:
there the notion of a mobile subject reflected a changed perception of
the subject and its relationship to the architectural object. Of particular
importance will be the conceptual precedent set by how these changes inscribed
themselves in Le Corbusier's work.
and of the impact it had on their thinking. The other historical thread
that needs pursuing relates to the development of the architectural promenade:
there the notion of a mobile subject reflected a changed perception of
the subject and its relationship to the architectural object. Of particular
importance will be the conceptual precedent set by how these changes inscribed
themselves in Le Corbusier's work.
In the Portugal of the 1940s and 1950s, two developments lent depth
to the feeling of at least one group of architects that the country's architecture
was falling into a set of empty stylistic patterns. The fascist dictatorship
of the Estado Novo (as the regime was called) had adopted a narrow range
of models by reference to which they were able to promulgate a homogeneous
state manner—monumental, even when small; quasi-neoclassical in appearance;
modern in functional considerations (figures 1 and 2). Following a familiar
fascist pattern, it proffered this architecture as the sole and unique
representation of a single and historically homogeneous Portugal. It did
not matter that this architecture, drawn from a version of the past adapted
to contemporary programmatic demands and the heroic goals of the state's
self-representation, looked little like any of the traditional Portuguese
architecture from which it purportedly drew its legitimacy. Just as the
representation of the state in the guise of a stern father leading a Portuguese
nation as if it were an extended family required the expression of real
political differences, so too did the architecture mandate an artificial
stylistic homogeneity. The state in a sense held language hostage, and
lent an exaggerated urgency to the suspicion of language's treachery.5 |
 3.
Vernacular farm building from Tras-os-Montes region of Portugal
3.
Vernacular farm building from Tras-os-Montes region of Portugal
|
The second development came from the increase in private and commercial
building in the country. Large numbers of citizens working abroad and returning
to Portugal to build homes or businesses—a pattern that persists in Portugal
today—had encouraged the construction of buildings in many imported architectural
styles.  Their roots within entirely different urban, climatic, technological, material,
and social circumstances, and the contrasting uniformity of many towns
and countrysides of Portugal, made these new buildings appear quite bizarre.
Their roots within entirely different urban, climatic, technological, material,
and social circumstances, and the contrasting uniformity of many towns
and countrysides of Portugal, made these new buildings appear quite bizarre.
Architects, led initially by Keil Amaral and later including Tavora,
sought in the traditional vernacular a model of architecture to which they
could look as a remedy. They eventually produced a thick survey called
Arquitectura Popular em Portugal, in which they documented, region
by region, the varieties of vernacular architecture in Portugal. What they
sought in the vernacular was a form of building without resort to "style,"
or what they called "constants," by which we can understand formal norms.
Although they chart typologies within the body of the book, in the introduction
they deny the importance of type. They are afraid that from types a "Portuguese
architecture" might be sought and reified into a code, just as the state
had done with its models. They flee from the stifling and betraying codifications
that are language. They do say that the buildings reflect, although not
in types or specific architectural elements, "something of the character
of our people" in terms of a tendency to domesticate and turn "humble"
certain traits of the baroque. Exactly what that is, which must be some
formal characteristic—simplification of contour, for instance—is purposely
left unsaid. Instead they point out the "strict correlation" in those buildings
"with geographical factors, as well as economic and social conditions."
They are "simply direct expressions, without intrusions nor preoccupations
with style to perturb the clear and direct consciousness of these relations."6
Paulo Varela Gomes, in his brief but excellent synopsis of Portuguese architecture,
has called the thinking reflected in this book a "metaphysic of the relation
between work and life."7
The vernacular is seen as the unmediated and, shall we say, prelinguistic
product of life and its conditions. I would again bring to mind Rosenberg's
idea of "American action painters"  whose work did not represent the being of the artist so much as
it was an unmediated trace, or record of the artist's life in action.8
These buildings are like tools, transparent to their human task (figure
3). They bear the logic that brought them into being: the task to be performed,
the hand that will need to grip them, and indirectly that aspect of the
society reflected by the very existence of the need to perform that task
to which the tool is dedicated. The sign is not yet broken into the arbitrary
relationship between the signifier and the signified.
whose work did not represent the being of the artist so much as
it was an unmediated trace, or record of the artist's life in action.8
These buildings are like tools, transparent to their human task (figure
3). They bear the logic that brought them into being: the task to be performed,
the hand that will need to grip them, and indirectly that aspect of the
society reflected by the very existence of the need to perform that task
to which the tool is dedicated. The sign is not yet broken into the arbitrary
relationship between the signifier and the signified. |
|
Whatever degree of truth there may be in the supposition that form
has a more natural relationship to "life" in the rural communities and
regions from which these architects drew their examples, the central fact
of unselfconscious reproduction and incremental modification of traditions
is lost and inaccessible to the very self-consciousness that goes in search
of it in the vernacular. If the vernacular were merely a model for how
to produce buildings in harmony with one's contemporary circumstances,
these architects' work might have been more like certain traditional strands
of modernism. They, like Hannes Meyer, might have tried to eliminate the
question of language by focusing exclusively on modern techniques of construction
and solutions to contemporary problems. But there was something in the
actual formal character of the vernacular that was appealing to them. |
 4.
Vernacular farm building from Minho region of Portugal
4.
Vernacular farm building from Minho region of Portugal
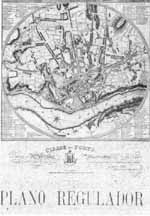 5.
Plano Regulador do Porto
5.
Plano Regulador do Porto
|
The architecture grew in an incremental way and not, as
they pointed out, with great concern for formal precepts. Buildings accommodated
themselves to the existing conditions of their sites. Buildings attached
to walls allowed themselves to be shaped by those walls (figure 4). Both
walls and, to a large extent, buildings allowed  themselves to be shaped by the contours of the land. Much of Portugal is
hilly or mountainous, and much of the building in towns and countryside
exhibits the highly irregular figures that result from this conformity
to the landscape. They created an angling, fragmented, mosaic pattern across
the countryside. Even in major towns, the streets are rarely straightened,
nor is the geometer's mark to be found in the squares. These too still
bear the geometry of original terrain-driven figures (figure 5). There
is then a general absence of an architecture of a priori geometrical form;
building maintains the legibility of the antecedent world into which it
is built—that is, the rolling forms of the earth—and its slow, incremental
pattern of addition and growth are visible; new building does not raze
old building. The vernacular has an archeological effect whereby its own
history and natural history are inscribed in its form. In this respect
it satisfies some of those objectives sought out by its investigators.
When Siza begins to practice in the late 1950s and early 1960s, many of
these characteristics will have an effect on the strategies he adopts.
How his work diverges from this model, however, will intensely reflect
the remoteness of the unselfconscious practices of these rural communities.
themselves to be shaped by the contours of the land. Much of Portugal is
hilly or mountainous, and much of the building in towns and countryside
exhibits the highly irregular figures that result from this conformity
to the landscape. They created an angling, fragmented, mosaic pattern across
the countryside. Even in major towns, the streets are rarely straightened,
nor is the geometer's mark to be found in the squares. These too still
bear the geometry of original terrain-driven figures (figure 5). There
is then a general absence of an architecture of a priori geometrical form;
building maintains the legibility of the antecedent world into which it
is built—that is, the rolling forms of the earth—and its slow, incremental
pattern of addition and growth are visible; new building does not raze
old building. The vernacular has an archeological effect whereby its own
history and natural history are inscribed in its form. In this respect
it satisfies some of those objectives sought out by its investigators.
When Siza begins to practice in the late 1950s and early 1960s, many of
these characteristics will have an effect on the strategies he adopts.
How his work diverges from this model, however, will intensely reflect
the remoteness of the unselfconscious practices of these rural communities. |





